Project management approaches are crucial in lowering risks and boosting sustainability in African development endeavours. By offering defined frameworks, these techniques assist speed planning, execution, and evaluation, ensuring projects accomplish long-term goals while minimizing obstacles. They enable better resource management, stakeholder participation, and adaptation to changing conditions, which are vital in meeting Africa’s particular development demands.
Importance of Project Management Methodologies in African Development
In the context of African development, where projects often confront difficult socio-economic, environmental, and logistical challenges, project management approaches offer the tools needed to handle these impediments. Frameworks like PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge), PRINCE2 (Projects in Controlled Environments), and Agile help project managers to successfully organise resources, communicate with local stakeholders, and adapt to uncertainties—all of which are crucial for sustainable growth. Furthermore, these approaches assist provide an organised strategy to controlling potential risks and assessing the environmental, social, and economic implications of development initiatives.
Enhancing Risk Mitigation through Structured Frameworks
Risk is inherent in development efforts, particularly in areas with changeable political and economic situations. Project management approaches establish frameworks that detect, assess, and eliminate risks before they become substantial hurdles. For example, PMBOK’s risk management processes contain phases for risk identification, qualitative and quantitative analysis, and reaction planning, which are critical for anticipating and limiting disruptions.
In African development, dangers can involve resource shortages, political instability, or poor infrastructure. By employing techniques like PRINCE2, which stresses extensive risk assessment and real-time monitoring, project teams can proactively handle these difficulties.
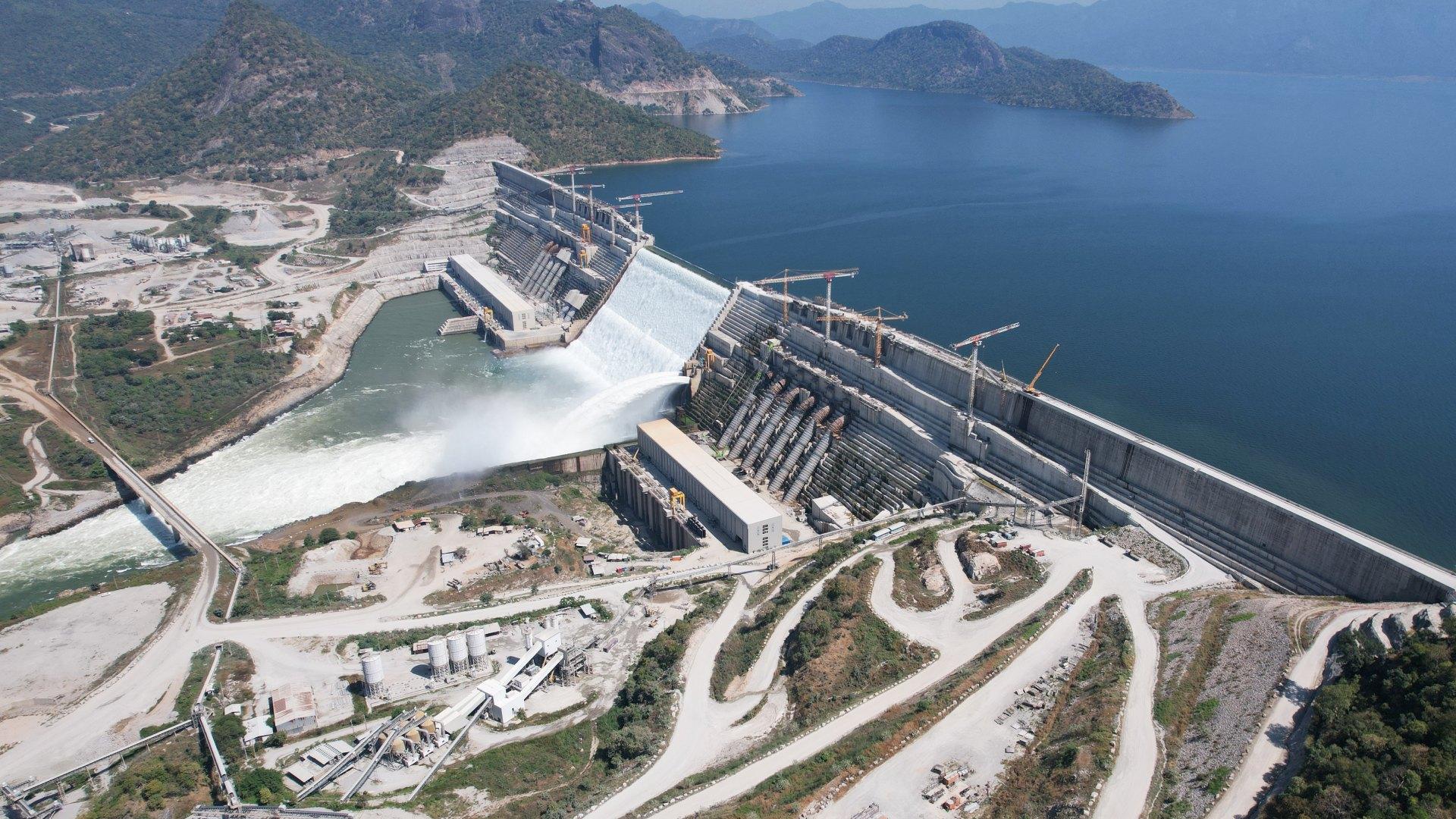

A case in point is the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) project, which faced significant geopolitical and environmental problems. Adopting structured risk management approaches helped project leaders to connect with different stakeholders, prepare for resource variability, and manage international concerns, thereby decreasing possible disputes and ensuring the project’s advancement.
Promoting Sustainable Resource Management
Efficient resource allocation is a cornerstone of sustainable project management, particularly in African regions where resources are often limited or unevenly distributed. Project management approaches give frameworks that help identify and allocate resources effectively, ensuring that development initiatives do not overdraw on local supply or harm ecological systems.
The Agile technique, for instance, is well-suited for managing projects in resource-limited contexts. By breaking down projects into smaller, manageable iterations, Agile allows teams to focus on urgent resource needs and make modifications as conditions change. An example of Agile’s impact is visible in community-led water and sanitation initiatives in Kenya, where resources might be unexpected. By employing Agile principles, project managers may adjust to resource availability, track consumption rates, and make incremental improvements that correspond with both short-term needs and long-term sustainability goals.
Ensuring Community Engagement and Stakeholder Collaboration
One of the primary issues in African development initiatives is ensuring that the interests of local communities and stakeholders are integrated into project goals. Project management techniques such as PRINCE2 stress stakeholder interaction as a vital element, helping develop trust and alignment between project goals and community requirements.
A well-known illustration of effective stakeholder involvement is Rwanda’s Vision 2020 Umurenge Program (VUP), which focuses on poverty reduction and infrastructure development. Using formal stakeholder engagement frameworks, project managers were able to integrate the program with local requirements, giving focused assistance and empowering people to take part in the development process. Such techniques assist reduce project delays, boost local ownership, and ensure that development achievements are sustainable and consistent with the objectives of the people they serve.

Adapting to Changing Conditions with Flexible Methodologies
African development projects typically confront changing conditions due to political transitions, economic volatility, or environmental concerns. Project management strategies such as Agile and hybrid approaches give flexibility that is crucial for reacting to changing situations. Agile’s iterative structure enables project teams to make incremental progress and adjust to changes without large disruptions.
For instance, in agricultural development projects across sub-Saharan Africa, weather conditions and market prices can fluctuate fast, impacting project schedules and resource needs. By employing Agile principles, project managers can respond to these transitions, executing modifications in real time to guarantee that projects remain feasible. This adaptability is vital for sustaining development projects that depend on fluctuating elements, such as agricultural output or community participation rates.
Monitoring and Evaluating Sustainability Outcomes
Project management approaches are crucial in tracking and analysing project outcomes, ensuring that sustainability goals are reached. Frameworks like PMBOK and PRINCE2 integrate monitoring and evaluation methods, which help examine the social, economic, and environmental effect of projects. In African development initiatives, this is vital for evaluating how projects contribute to long-term goals, such as poverty reduction, environmental conservation, and economic resilience.

For example, in renewable energy projects across Africa, where solar and wind energy installations are more popular, systematic evaluation processes help analyse project performance and sustainability. By employing PMBOK’s structured evaluation approaches, project teams may quantify energy output, cost savings, and community impact, offering insights that guide future projects and ensuring that renewable energy programs are scalable and sustainable.
In sum, project management approaches play a critical role in minimising risk and supporting sustainable growth in African development endeavours. By offering formal frameworks for planning, resource management, stakeholder participation, flexibility, and assessment, these approaches enable development projects achieve their goals while minimizing environmental and social consequences. As Africa continues to pursue ambitious development goals, implementing sound project management methods will be vital to ensure that progress is both resilient and sustainable.
